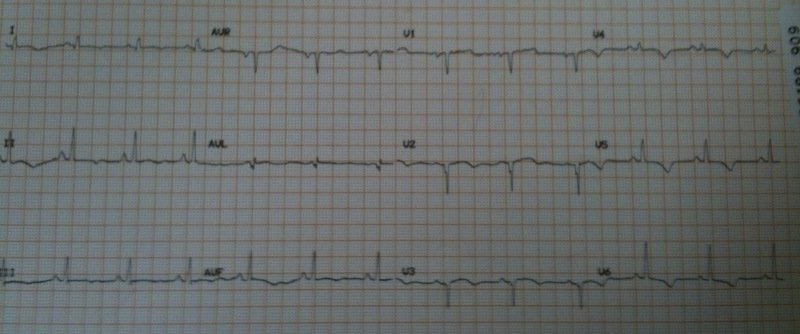
A 79 yo female presented with crescendo angina. She has a history of anterior STEMI a few years ago treated with tPA. She has DM, HTN, and smokes. She was pain free at the time of this ECG (ECG #1):
It is always wise to compare with a previous ECG, but only with knowledge of the normal evolution of post-MI ECGs. Here are the previous ECGs:
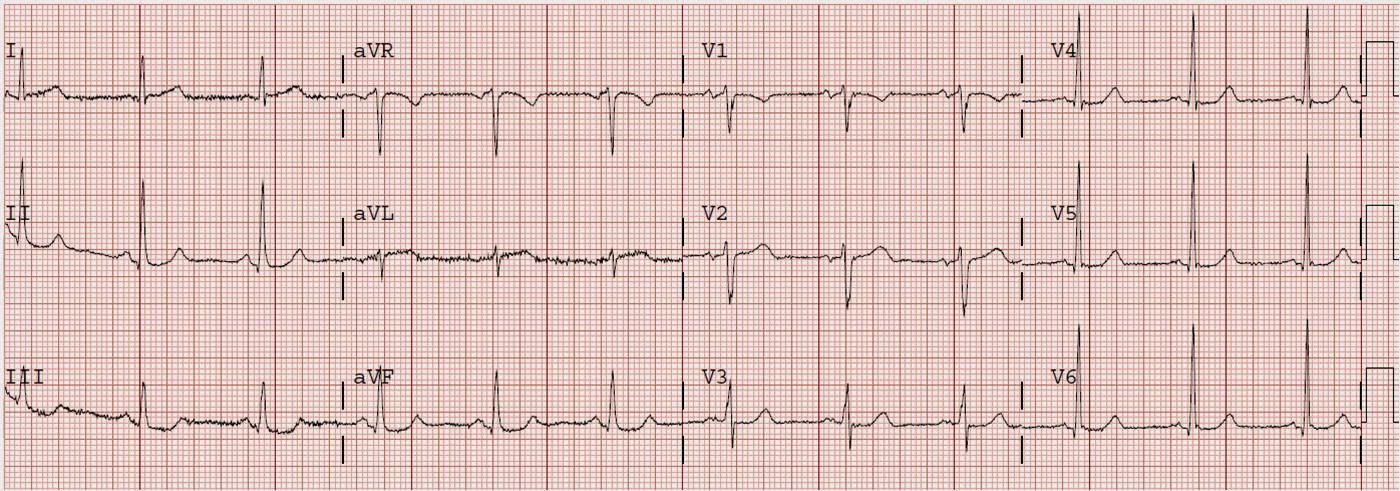
ECG #2 is the last ECG, recorded after resolution of the previous anterior STEMI shown below.
ECG #3 is the one obviously diagnostic of anterior STEMI (before evolution to the LV aneurysm morphology above:
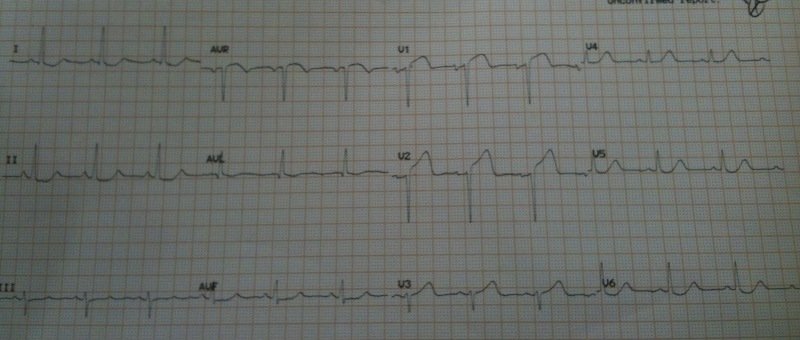 |
| Obvious anterior STEMI |
Why are the T-waves upright now (ECG #1)? Is it pseudonormalization? No:
In the normal evolution (over months) of the post-MI ECG, T inversion (usually) becomes upright. On the other hand, pseudonormalization happens acutely (within the first week or two), usually after a reperfused MI and is due to re-occlusion. The T-waves are large and hyperacute.
Thus, we expect that the T inversion after an MI will be resolved if we get an ECG much later.
So ECG #1 is not due to pseudonormalization. If the patient has ongoing symptoms (unlike this one), serial ECGs are indicated because hyperacute T-waves and ST elevation may develop, but this ECG#1 represents the expected ECG evolution of this patient with previous transmural MI. This patient ruled out for MI by troponin.
.